Understanding Septal Infarct: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Septal infarct is a medical condition that affects the septum, a wall of tissue that separates the left and right sides of the heart. It occurs when the blood supply to the septum is disrupted, leading to tissue damage and potential complications. In this blog post, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for septal infarct.
Understanding Septal Infarct
Septal infarct, also known as myocardial infarction of the interventricular septum, occurs when the blood flow to the septum is reduced or completely blocked. This lack of blood flow deprives the septal tissue of oxygen and nutrients, causing cell death and leading to infarction.
Causes of Septal Infarct
- Coronary Artery Disease: The most common cause of septal infarct is coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD is characterized by the build-up of plaque within the coronary arteries, which restricts blood flow to the heart muscle. When the plaque ruptures or a blood clot forms, it can block the blood supply to the septum, resulting in an infarct.
- Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis, the hardening and narrowing of the arteries due to the accumulation of fatty deposits, can contribute to septal infarct. The narrowed arteries reduce blood flow, increasing the risk of a clot formation that can lead to septal infarction.
Symptoms of Septal Infarct
- Chest Pain: One of the most common symptoms of septal infarct is chest pain or discomfort. The pain may be severe, radiating to the arm, jaw, or neck. It is typically described as a crushing or squeezing sensation.
- Shortness of Breath: Septal infarct can also cause shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion or rest. This symptom occurs due to the reduced pumping efficiency of the heart.
Diagnosing Septal Infarct
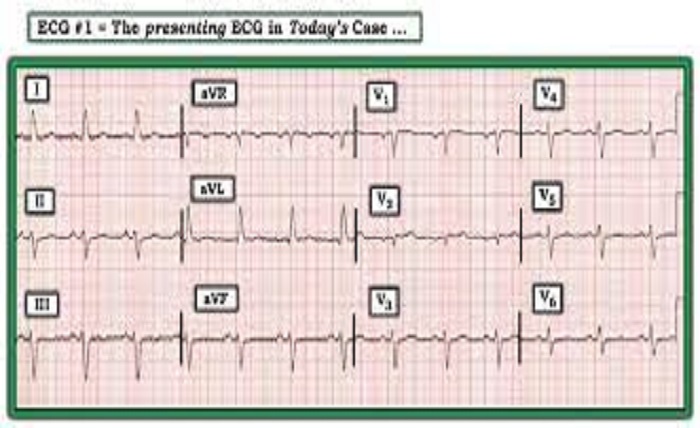
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG is a common diagnostic test used to detect septal infarct. It records the electrical activity of the heart, and specific changes in the ECG pattern can indicate an infarction in the septal region.
- Echocardiography: Echocardiography uses sound waves to create images of the heart. It can help visualize any structural abnormalities or wall motion abnormalities that may suggest septal infarct.
Treatment Options for Septal Infarct
- Medications: Medications play a crucial role in the treatment of septal infarct. Antiplatelet drugs, such as aspirin, can prevent blood clot formation. Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors may be prescribed to reduce the workload on the heart and improve its function.
- Revascularization Procedures: In severe cases of septal infarct, revascularization procedures may be necessary. These procedures aim to restore blood flow to the affected area. Angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery may be performed to open up blocked arteries and improve blood supply to the septum.
Lifestyle Changes and Cardiac Rehabilitation
To prevent further complications and promote heart health, individuals with septal infarct are advised to make certain lifestyle changes. These may include adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, managing stress levels, and attending cardiac rehabilitation programs.
Conclusion:
Septal infarct is a serious condition that can have significant implications on heart function. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking prompt medical attention are essential for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.





